Polygon, originally known as Matic Network is an Ethereum scaling solution. It uses Layer 2 sidechains to increase the speed and efficiency the Ethereum network. The Polygon Network enhances the Network’s transaction processing speed and reduces transaction costs, also known as gas fees.
As its name suggests, Polygon has a broad scope – it provides a framework for launching sovereign blockchains and decentralized applications and building interconnected blockchain networks.
Polygon kept its MATIC token after Matic Network’s rebranding. It was used to power Matic Network as well as serve as a utility token.
Polygon came into existence when Ethereum, the largest blockchain network, became congested with transactions as its demand in the emerging decentralized finance (and NFTs) skyrocketed. Ethereum raised network usage fees, making it too costly for both average users and developers who run their apps on top of its ledger.
Uniswap is a leading decentralized cryptocurrency exchange. The transaction fee for transactions was $1,000 at one point. That’s a huge difference from the $0 transaction fee charged by centralized counterparts.
So, how has the Polygon Network become one of the leading alternatives to Ethereum’s gas-cost problem? What is the reason that MATIC, its native token has risen by more than 10,500% within a single year?
You can read on for all the details about Polygon and MATIC tokens.
What is Polygon?
Polygon, formerly known as Matic Network, was rebranded in February 2021. It refers to itself as “Ethereum’s internet of blockchain.” The Polygon Network is a blockchain scalability platform for connecting and building blockchain networks compatible with Ethereum.
Polygon (formerly Matic Network) is also categorized as a layer-2 aggregator aiming to offer scalable solutions to support a multichain ecosystem of Ethereum-compatible blockchains with superior interoperability.
The platform’s core component is a modular, flexible framework (dubbed Polygon SDK) that enables developers to build and connect the so-called Ethereum Layer-2 infrastructures like Optimistic Rollups, zkRollups, Plasma, and Validium.
Polygon, which is Plasma-based, is an aggregator and layer-2 solution to Ethereum. It supports infrastructure development, helping Ethereum scale. Developers can create secure, decentralized, and scalable apps (dApps), off-chain. Polygon’s implementation of Plasma is called Polygon Plasma Chains. Polygon Plasma Chains not only provide a platform for dApps but also enable faster and cheaper transactions by offloading the transaction from the main Blockchain into secondary chains.
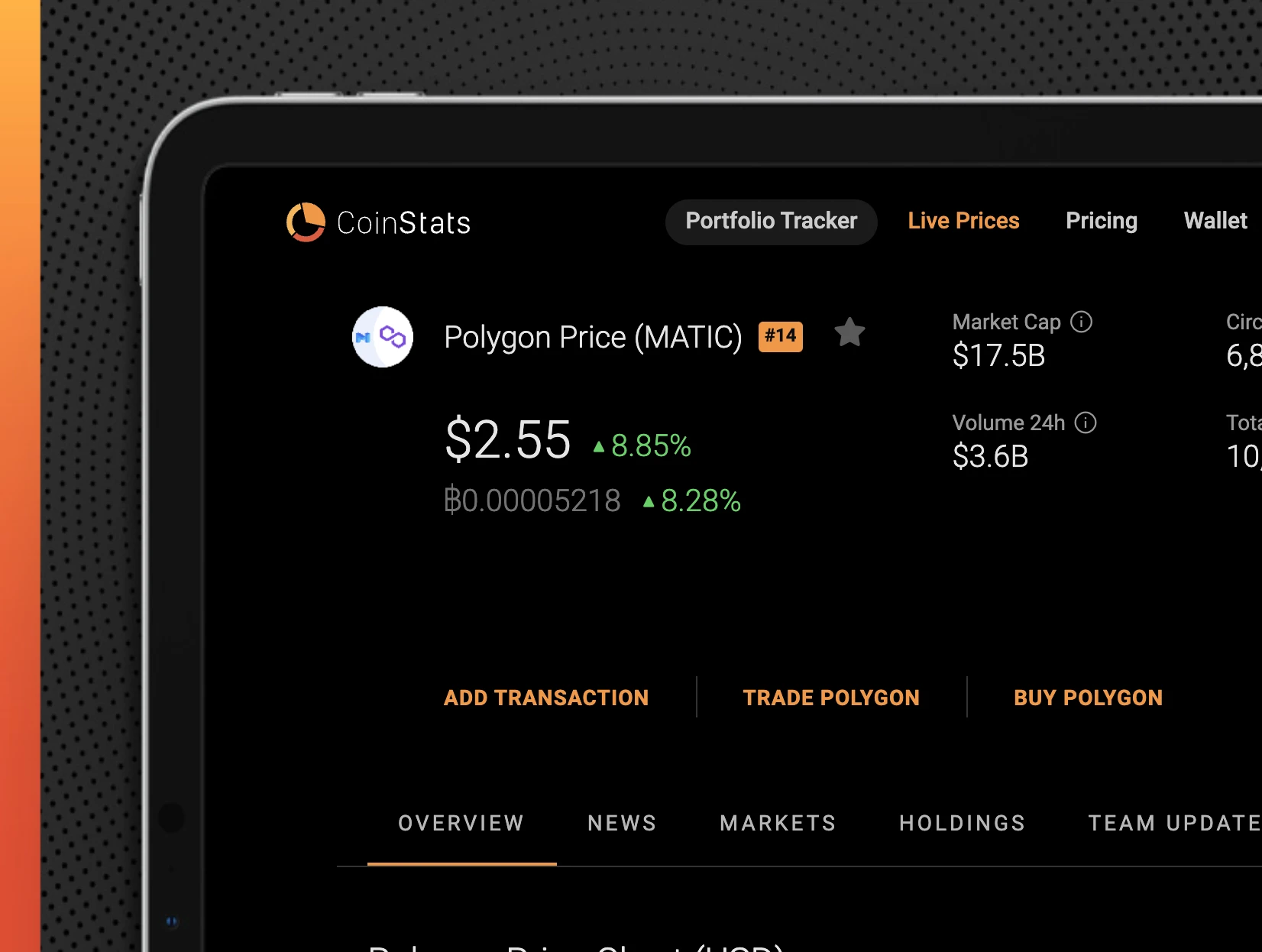
MATIC is Polygon Network’s native token, with a $16.1 billion market cap, making it the 14th largest cryptocurrency. MATIC can hold a maximum of 10,000,000 coins. It has an average circulating supply around 6.87 billion.
MATIC is used to power the Polygon Network and serves as a utility token. It’s the Network’s main transactional currency and is also used as collateral in staking, enabling users to participate in Polygon’s consensus mechanism to validate transactions in return for MATIC tokens.
Polygon How It Works
Polygon (formerly Matic Network) consists of a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) sidechain variant, known as “commit chain,” which supports smart contract development, and a Plasma-based entry ramp for routing Ethereum-to-Matic sidechain transactions.
The project employs an independent set of validators that don’t share the security of Ethereum, a general standard for layer 2s. The validators make periodic Matic PoS changes to Ethereum, which is done through a process known checkpointing. This allows transactions to be completed. While the said approach uses Ethereum as a settlement layer, it doesn’t provide complete protection against malicious validators corrupting the checkpointing process.
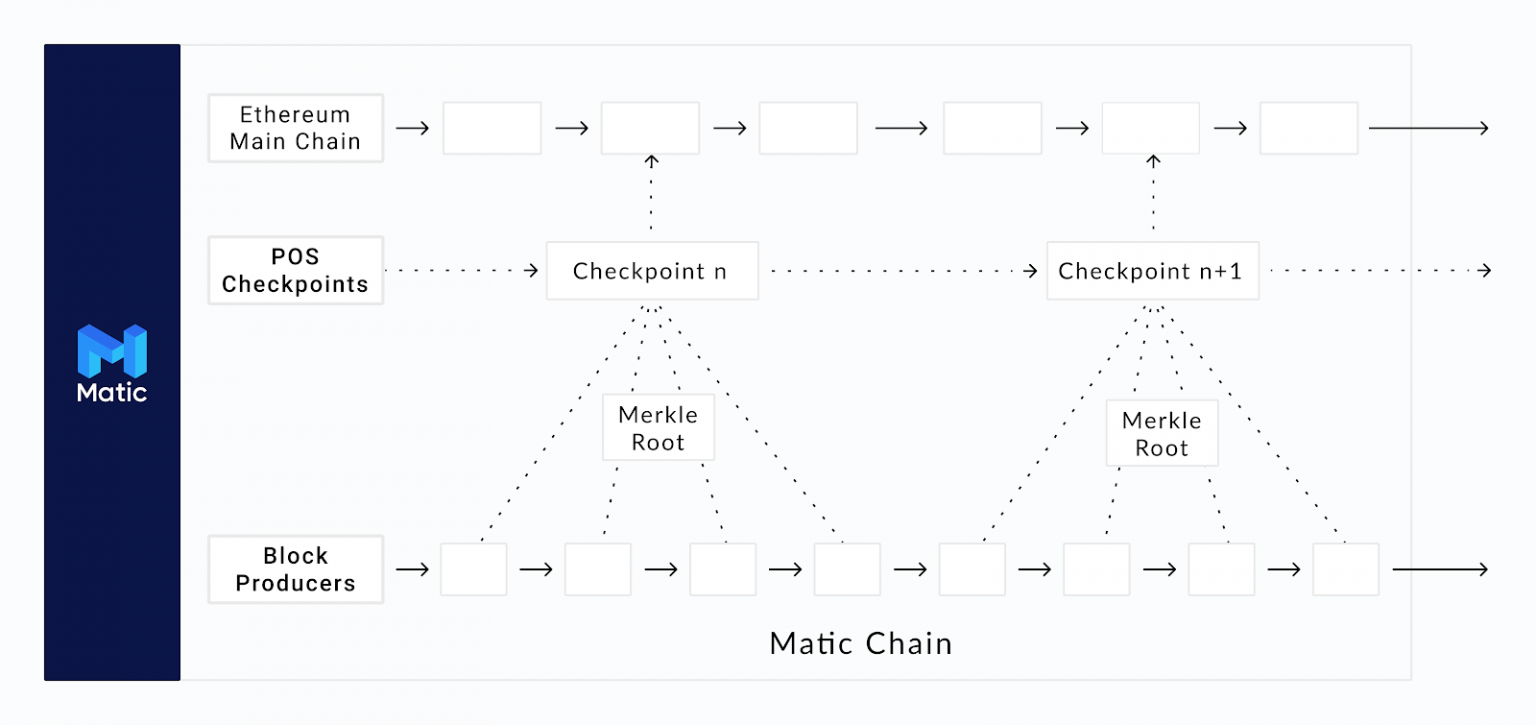
But, even though it is only a layer 2 in spirit Polygon’s Matic PoS chain is currently one of the few realistic alternatives to Ethereum scalability issues. Additionally, many protocols and developers have opted to use Matic PoS to store block space instead of waiting to find a rollup solution due to the constant demand.
These protocols can be used to create gamified financial collectibles (such as Aavegotchi), virtual worlds (such as Decentraland) and gambling markets like Polymarket and SportX. Somnium Space is another Polygon-based application.
In addition to the Matic PoS Chain and Plasma Chain, the Network is working on developing further scaling infrastructure for Ethereum, with Optimistic Rollups being the next major update.
MATIC Tokens: What Role Does It Play?
MATIC serves as a staking token for Polygon’s PoS blockchain, making Polygon a unique layer two solution, compared to its competitors, such as Matter Labs (zkSync), Off-chain Labs (Arbitrum), Starkware, and Optimism that have generated financial backings from traditional venture capitalists. Meanwhile, some app-specific layer 2s have tokens, such as Loopring and ZKSwap, but those tokens aren’t used to compensate node validators, at least for now.
Polygon has an advantage because MATIC, one of the few seasoned layer 2 tokens on the market, is based on the facts above. Retail users are exposed to the anticipated rise in layer two options, as other solutions chose the VC route. This is why MATIC’s recent performance has been damn phenomenal, up over 10,000% year-to-date.
Nonetheless, it’s important to mention that MATIC is not an actual governance token since voting is limited to adjusting validator parameters. Also, it’s inflationary, with the Polygon protocol holding the right to add approximately 50% to the current tokens outstanding.
To sum up, MATIC’s use-case provides retail traders enough reason to speculate on its price growth, which explains the process of buying Polygon tokens.
MATIC: How to Purchase Polygon Tokens
Polygon’s MATIC is available to purchase or sell on many leading cryptocurrency platforms, including Coinbase Pro, Binance, Kraken, Cex.io etc.
To secure MATIC tokens, follow our steps-by-step instructions.
Step 1. Create an account online. Sign up for a crypto exchange that accepts the MATIC token if this is your first time in the cryptocurrency world.
To register for crypto exchanges, you will need to provide personal data such as your name, address, phone number and proof of ID. Standard KYC procedures will be necessary.
Step 2 – Get a wallet. A cryptocurrency wallet can be described as a safe place to safely keep your crypto investments. While software wallets, such as Metamask or Coinbase Wallet are great options for investors, it is a good idea to consider acquiring a hard drive wallet. As a professional-grade secure wallet, a Ledger wallet like Ledger nano S or X is strongly recommended. This allows you to transfer your MATIC tokens directly to another address.
Step 3: Complete your order. There are many ways you can buy MATIC depending on which exchange platform. It is possible to purchase Polygon tokens using your credit/debit cards. Otherwise, you can first purchase dollar-pegged stablecoins (Tether, DAI, Circle USD) via fiat currency and later trade them for MATIC via exchanges’ in-house trading platforms. Because stablecoins enable faster trades so traders don’t miss lucrative investment opportunities.
For those who value anonymity more than ease, there is an alternative. They can buy Polygon’s MATIC tokens via decentralized exchanges like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and others. Connecting their Metamask wallets to these platforms is all they have to do. The wallet will be loaded with cryptos like Ether and Tether. They can trade the cryptos directly via MATIC through their chosen decentralized exchange.
Conclusion
Polygon, a project that focuses on scaling and interoperability of blockchains, is regarded as one the most innovative. Moreover, Polygon is the only scalability solution to fully support the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which means that dApps built in the Polygon Network will benefit from Ethereum’s Network effect without sacrificing its robust security. Polygon’s flexibility is key in enabling developers to create truly interoperable dApps that can benefit from the attributes of multiple interconnected blockchains.
Lastly, since Polygon offers multiple scaling mechanisms, they don’t risk becoming obsolete if one particular solution becomes the industry standard in the future.
The value of Polygon’s scaling technologies is also reflected in MATIC’s price action, as the token surged during two major crypto market corrections this year.
So while Ethereum’s scaling market becomes too crowded in the coming months, Polygon’s first-mover advantage, community-driven backing, and timely axis could be enough to give it an edge over its competitor.
