If you want to venture into the world of decentralized finance (DeFi) and don’t know which exchange to pick – you’ve come to the right place!
This article will explain everything about Uniswap – from what it is and what made it popular, to how it works and if it’s safe. Let’s get into it!
Executive Summary
- Uniswap is an open-source decentralized exchange (DEX) initially built on top of Ethereum’s blockchain, that now supports numerous chains.
- This is an automated liquidity protocol. It does not have an order book but provides liquidity in a uniquely unique manner.
- Everybody has the ability to list and trade tokens or stakes as well as take part in the governance processes of Uniswap.
- Uniswap was through several iterations. Uniswap is now on the 3rd one (UniswapV3).
- Uniswap, currently the biggest AMM DEX with its UNI token the 19th largest cryptocurrency market cap.
What exactly is Uniswap?

Uniswap is an open-source decentralized exchange (DEX) initially built on top of Ethereum’s blockchain, that now supports numerous chains.
As a protocol that is decentralized, there is no listing process. This means anyone can list tokens on the exchange provided they offer liquidity to traders via a liquidity pool. Uniswap doesn’t charge listing fees.
Trading on Uniswap can be described as an automated liquidity protocol. The exchange does not have an order book. Instead, the exchange created its own system for determining prices of buying and selling, as we’ll explain in this article.
Who are the Founders and Chief Executive Officers of Uniswap
Hayden Adams was the one who created and launched the original version of Uniswap. In 2018, Hayden Adams launched the first version of Uniswap.
Uniswap was created for a reason.
Uniswap was founded in reaction to centralized exchanges that had shown inefficiencies in decentralization and security. On top of that, other DEX solutions were highly illiquid and not very user-friendly, which created space for Uniswap’s automated liquidity idea.
It gave rise to a crypto-sector with a low trading fee, high decentralization levels and resistance to censorship, along with great liquidity.
Uniswap is a popular choice.
Uniswap’s decentralized exchange concept has been popularized largely due to its simple-to use and intuitive design. Also, users don’t have to worry anymore about inadequate liquidity.
It’s easy to simply connect a crypto wallet, buy or sell your crypto, or deposit your digital assets to a liquidity pool.
What is the Uniswap UNI Token?

The UNI token serves as the core of the Uniswap Protocol. It serves as the ecosystem’s governance token. It was first distributed to protocol users that provided liquidity in the early days of its existence, and also to regular users.
The UNI token is now a way for users to take part in the governance of the future protocol. Voting on new tokens or upgrading the Uniswap stock exchange is one example.
Although it’s far down from its $43.16 all-time high, UNI is now the 19th largest cryptocurrency by market cap.
Is There a Circulation of Uniswap (UNI), Tokens?
Uniswap has a maximum token stock of 1,000,000,000 UNI. All UNI tokens should be available within four years. 75% is currently in circulation when it comes to circulating supply.
Uniswap has announced an inflation rate increase of 2% annually to keep the network active after four years since protocol launched.
60% of the UNI token supply went to Uniswap community members. Rest 40% of the UNI token supply will be distributed to members of the team, investors, and advisors who helped in this project.
What is the value of Uniswap UNI Tokens?
Uniswap’s cryptocurrency, UNI, plays a key role in maintaining and operating its network.
Users who hold UNI tokens have the ability to help govern the protocol, and vote on proposals that might further Uniswap’s development.
The protocol’s aim is to decentralize decision-making, thus the direction of the protocol is managed by governance votes from UNI token holders rather than by a centralized team or company.
Uniswap achieved that vision by distributing 60% of its total supply directly to users. Most importantly, it sent 400 UNI every user by September 1, 2020. Additionally, users who have contributed to liquidity pools were rewarded with tokens.
How Does Uniswap Work
Now that we have covered what Uniswap is, we are ready to cover its ecosystem’s inner workings.
We have three major parts to the Uniswap eco-system:
- Uniswap liquidity pool (liquidity provision).
- Trading in cryptocurrency
- Uniswap Governance
Uniswap Liquidity Pools
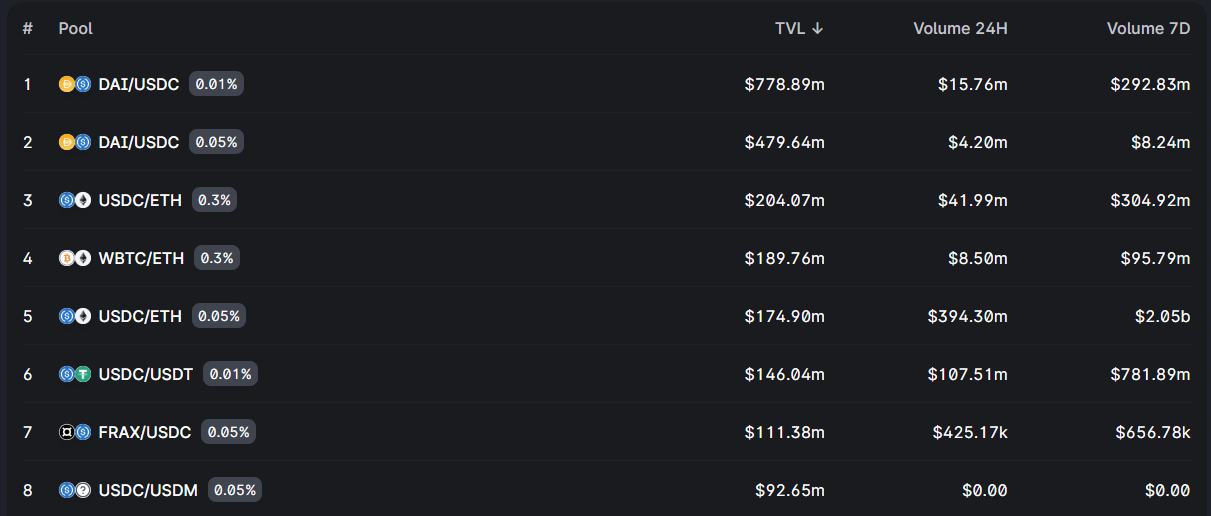
As we mentioned before, Uniswap doesn’t have any order books as centralized exchanges do. Instead it uses a series of smart contracts, called Automated markets makers (AMM).
An automated market maker is a smart contract that holds liquidity reserves. In other words, you need a liquidity pair before we can trade between two crypto currencies. A liquidity provider deposits two equivalent tokens into a pool to achieve this.
The price of cryptocurrencies changes when people sell more than they buy. This can increase or decrease the value of any particular cryptocurrency in a protocol. The majority of smaller cryptocurrencies can be paired with Ethereum (ETH) or other stablecoins.
Others can deposit money to the liquidity pool and provide liquidity. They receive a liquidity pairing NFT in return for their part of the liquidity pool. The portion of their pool’s transaction fees they receive (Uniswap charges a % per trade) is shared with them.
Uniswap Cryptocurrency Trading
When it comes to trading cryptocurrencies on Uniswap, we can approach it from the user’s perspective.
When we wish to trade one cryptocurrency for another we first need to connect our Web3 wallet. Next, find the appropriate liquidity pairing for that currency. The trade will only cost 0.3% once we’ve done this.
We must also pay close attention to how deep the liquidity pool is and the order size. The larger the order is, the larger the effect on the pool’s liquidity. The impact of each order is also greater if the liquidity pool depths are smaller. Slippage, which can cause large price swings mid-trade is possible.
Uniswap lets its users choose the slippage limit they will accept in order to safeguard them from accidental slippage.
Uniswap Governance

As explained previously, any UNI token holder can take part in the decision-making process at the Uniswap Protocol.
They can do so by voting on different proposals that will determine the future of Uniswap’s development. The protocol does require that you have a minimum 1% share of the total UNI supply to make proposals to the Uniswap Networks.
Example of Uniswap
Let’s bring the inner workings of the Uniswap protocol closer to you with an example. Let’s say we want to buy USDC with ETH, meaning we need to access the USDC/ETH pool.
We’ll call the USDC portion of the pool “x” and the ETH portion “y”. Uniswap multiplies the quantities of both cryptocurrencies within a pool to determine the total liquidity. Let’s call this k. According to their whitepaper, the core idea behind Uniswap is that k is constant, meaning that any changes to the x or y will change the price of the cryptocurrency. The formula to determine the total liquidity of the pool is:
x * y = k
We can use USDC/ETH to buy 1,500 USDC tokens for the 1ETH that we have. The 0.3% fee is paid and we receive our 1,500 USDC tokens. The trade made by us resulted in 1 ETH and 1,500 USDC being less. Because the pool must maintain total liquidity, there is no way to change the USDC/ETH price. This means USDC has become slightly more expensive after the trade. ETH however is somewhat less costly.
Impermanent Loss in Uniswap
Uniswap liquidity providers are subject to permanent loss. To provide liquidity to a liquidity bank, you must first deposit both the cryptocurrencies in that pool. As the value of one cryptocurrency fluctuates, so does the balance within the pool. It might have made more sense to hold just the two cryptocurrency without providing liquidity. Impermanent Loss is the result of this type of event.
As the title suggests, impermanent losses are temporary until your money is withdrawn. It is important that liquidity providers keep this in mind as they must estimate their profits. The risk of permanent loss is always there.
Uniswap v1
Even though it wasn’t the first DEX, Uniswap was certainly the first one to catch the eye of crypto enthusiasts. Before Uniswap EtherDelta had been the most popular DEX. But, the order book model was flawed. It had high costs and poor user experiences, as well as a low liquidity.
Uniswap’s V1 was the first decentralized exchange that introduced a non-order book model, which is one of the main reasons it gained traction.
Uniswap v1 could only support ETH/ERC-20 trading pairs. You were able to swap Ether for any other ERC-20 token. You could trade two ERC-20 tokens if you trade the first token you received for Ether, then trade that token back for the second ERC-20 token.
Uniswap vs. Uniswap X3
As we mentioned, Uniswap went through three phases since its initial release. Uniswap V2 introduced ERC-20/ERC-20 pairs to make it easier for you to exchange your non-Ethereum altcoins. Uniswap V2 introduced a decentralized online price feed from Oracles. Uniswap added a protocol fee that took 0.5% from the 0.3% trading fees to help fund future development.
It is now in its third iteration. Uniswap V3 brings many enhancements to the protocol.
- Capital efficiency
- Flexibility fees
- Uniswap LP NFT tokens
- Oracles for advanced purposes
- License modifications
Capital Efficiency
Capital efficiency is one of the greatest improvements made by Uniswap V3.
A majority of AMM smart contracts are capital-inefficient. Funds deposited to AMM smart contracts were frequently sitting in idle. This resulted in Uniswap having large amounts of money sitting in its pool, but daily volumes being several times less.
Uniswap V3 solved this problem by allowing liquidity providers to set custom prices for the liquidity they provide. This allows pools to retain certain price ranges with less liquidity.
This improvement has brought Uniswap closer to order book exchanges, as liquidity providers could choose the price range they want to be in – which looks a lot like a limit order on traditional centralized exchanges. The protocol retained its original identity which helped it gain so much popularity.
Additionally, this meant that liquidity providers that used a “set it and forget it” strategy would earn far less than those that optimized their price ranges.
Flexibility in Fees
Uniswap v1 introduced a flat 0.30% fees structure. 100% of this goes to liquidity provers. Uniswap v2 introduced a 0.05% protocol charge that could be switched on/off depending upon the wishes of users.
Uniswap v3 offers community-governed flexibility via multiple fees tiers
- 0.05% – expected for stablecoin pools
- 0.30% – for standard pools like ETH/USDC
- 1.00% – for exotic pairs
The Uniswap Team then added more flexibility, allowing users the ability to vote for additional fees.
Uniswap LP NFT tokens
As liquidity providers are now able to choose their custom price ranges, the prior model of liquidity pair tokens wasn’t going to work. Uniswap V3 therefore introduced non-fungible tokens that can be used to represent custom range liquidity providers.
Oracles for advanced purposes
One of the most important changes in the back end was the handling of oracles by Uniswap. This improvement, without going too in depth, made it simpler and more affordable to make advanced oracles. It also reduced the cost of maintaining the oracles’ gas consumption by as much as 50%.
License modifications
One controversial change made by Uniswap V3 is the modification in smart contract licensing. Due to its open-source nature, Uniswap V2’s rising popularity has brought numerous Uniswap clones that just copied the code and changed branding.
Uniswap’s V3 has introduced a license that would prevent copycats from stealing the code, thus protecting the protocol from being copied, but also hurting the open-source philosophy of blockchain technology.
Uniswap on Layer 2.
Uniswap was too costly for many users due to the rising transaction fees on Ethereum in 2021.
Uniswap developed a layer 2 call solution, called Optimistic rolling up. As layer 2 solutions benefit from the main layer’s security, Uniswap was still as secure as before, while providing users with a cheaper solution for their day-to-day swaps.
Uniswap also launched their protocol for the Polygon blockchain in December 2021.
Uniswap currently supports many blockchains such as Ethereum and Polygon. Optimism. Arbitrum. Celo. More will be added in the near future.
What Makes Uniswap Money?
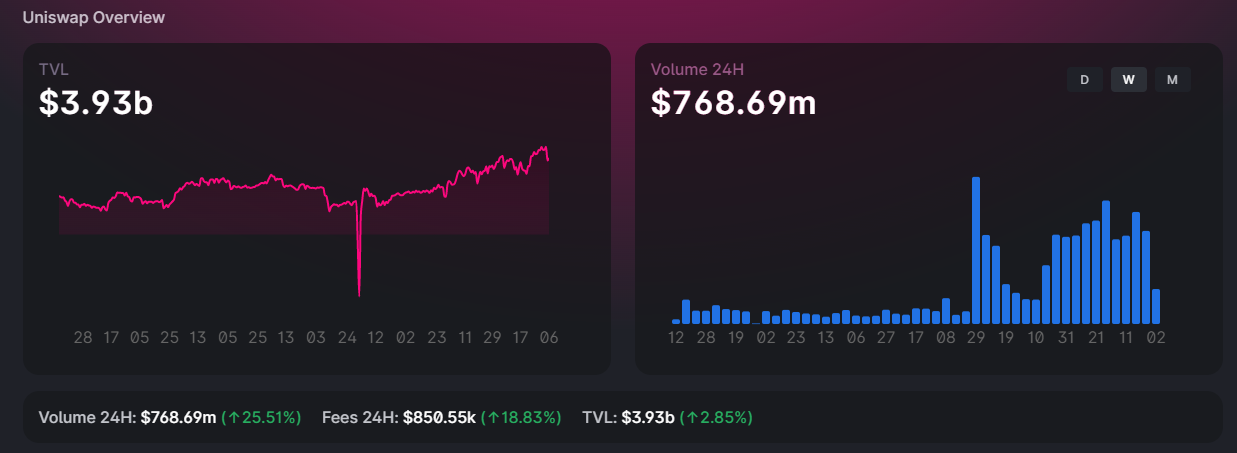
Uniswap makes its money basically in two ways. Protocol fees and UNI token appreciation.
Uniswap users can choose to disable protocol fees. This takes a small portion of the trading fees and puts it toward future protocols development. Although it might seem insignificant, Uniswap generated over $1 billion of revenue in 2021. Despite the fact that most revenue was spent on liquidity providers, the company managed to make $40 million.
The appreciation of UNI token is the other source of income for Uniswap or its founders. 20% of all UNI tokens are held by employees at Uniswap. This is a huge profit for the Uniswap staff as any token appreciation means huge profits. The current market capitalization is $4.75 Billion. Uniswap employees own well more than $1 billion worth of UNI tokens.
Is Uniswap a safe option?
Uniswap, a decentralized liquidity pool and exchange that operates on Ethereum, has been proven to be a reliable exchange. It borrows security from the Ethereum blockchain due to its centralization and built on Ethereum.
Unlike centralized exchanges, Uniswap has no custody over users’ funds, as well as no central server to hack or gain access to users’ funds.
In order to ensure liquidity, funds must be placed into an audited and highly secure smart contract. The same crypto wallet can only remove any funds that you have deposited.
Uniswap’s smart contracts have been thoroughly tested and audited by large auditing firms. Uniswap also offers a bug bounty program that rewards anyone who finds bugs and encourages them to report them to the team, rather than abusing them.
Uniswap is secure as long as your wallet remains safe.
Bottom line
Uniswap, a decentralized AMM exchange on Ethereum Blockchain and the crypto sector is the biggest. The market currently has 43.7% for the exchange.
Uniswap’s user-friendly and intuitive design, innovative features, and great reward programs have made it what they are today. Uniswap is a pioneer in decentralization, censorship resistance and other benefits. The industry’s most respected name, Uniswap is known for its intuitive smart contract and UI design. This made it the DEX protocol many others have followed.
While majorly affected by the skyrocketing Ethereum fees in 2021, the protocol is hoping to benefit from Ethereum’s scalability solutions.